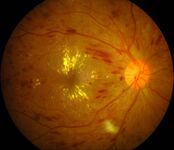
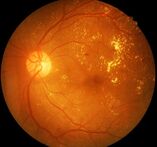
People with diabetes may face several eye problems as a complication of this disease. They include cataracts, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy, which is the leading cause of blindness in American adults ages 20–74. Anyone with diabetes is at risk of getting diabetic retinopathy. The longer someone has diabetes, the more likely he or she will get this eye disease. Between 40 and 45 percent of those with diagnosed diabetes have some degree of diabetic retinopathy.
In its early stages, diabetic retinopathy has no symptoms. A person may not notice vision changes until the disease advances. Blurred vision may occur when the macula swells from the leaking fluid (called macular edema). If new vessels have grown on the surface of the retina, they can bleed into the eye, blocking vision.
If you have diabetes, be sure to have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year. Diabetic eye disease can be detected early and treated before noticeable vision loss occurs.
In its early stages, diabetic retinopathy has no symptoms. A person may not notice vision changes until the disease advances. Blurred vision may occur when the macula swells from the leaking fluid (called macular edema). If new vessels have grown on the surface of the retina, they can bleed into the eye, blocking vision.
If you have diabetes, be sure to have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year. Diabetic eye disease can be detected early and treated before noticeable vision loss occurs.